Rolling Cube
Problem
You want to make a rolling cube in 3D.
Solution
Rolling a cube is trickier than it seems. You can’t just rotate the cube around its center:
Instead, the cube needs to be rotated around its bottom edge.
Here’s the tricky part: which bottom edge? It depends on which direction the cube is rolling.
In preparing this recipe, I experimented with a few different solutions to this problem:
- Pure math - calculating and applying rotation transforms
- AnimationPlayer - using animations to key the rotations and offsets
- Helper nodes - using Spatial(s) as rotation helpers
They all worked fine, but I found the last option the most flexible and easiest to adapt, so that’s what we’ll do here.
Node setup
Cube: KinematicBody
Pivot: Spatial
Mesh: MeshInstance
Collision: CollisionShape
Tween: Tween
You can do this with RigidBody, KinematicBody, or Area as your collision node. There will be minor differences in how you handle movement. Which node you choose should depend on what other behavior you want in your game. For this recipe, we’re only concerned with the movement.
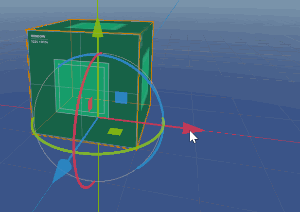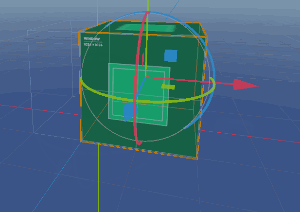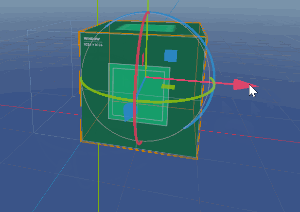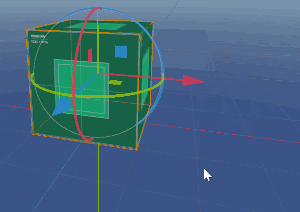
By default, everything will be centered at (0, 0, 0) so the first thing we’re going to do is offset everything so that the bottom center of the cube is the KinematicBody’s position.
To do this, move the mesh and collision nodes up to (0, 1, 0), leaving the rest where they are. Now when you select the root node, its position will be the bottom of the cube:
Now when you want to roll the cube, you’ll need to move the Pivot one unit in the direction you want to move. Since the mesh is attached, move it the opposite amount. For example, to roll to the right (+X), you’ll end up with this:
Now the pivot node is at the correct edge and rotating it will also rotate the mesh.
Movement script
The movement is broken in to 3 steps:
Step 1
Here we apply the two offsets shown above: shift the Pivot in the direction of movement, and shift the Mesh in the opposite direction.
Step 2
In this step we animate the rotation. We find the axis of rotation using the cross product of the direction and the down vector. Then we use the Tween to animate rotating the pivot’s basis. We use yield() to wait for the animation to finish.
Step 3
Finally, we need to reset everything so that it’s ready to happen again. In the end, we want to have the cube moved 2 units in the chosen direction (for a cube of size 2) and the pivot and mesh back at their original positions.
extends KinematicBody
export var speed = 4.0
onready var pivot = $Pivot
onready var mesh = $Pivot/MeshInstance
onready var tween = $Tween
func _physics_process(_delta):
var forward = Vector3.FORWARD
if Input.is_action_pressed("up"):
roll(forward)
if Input.is_action_pressed("down"):
roll(-forward)
if Input.is_action_pressed("right"):
roll(forward.cross(Vector3.UP))
if Input.is_action_pressed("left"):
roll(-forward.cross(Vector3.UP))
func roll(dir):
# Do nothing if we're currently rolling.
if tween.is_active():
return
## Step 1: Offset the pivot
pivot.translate(dir)
mesh.translate(-dir)
## Step 2: Animate the rotation
var axis = dir.cross(Vector3.DOWN)
tween.interpolate_property(pivot, "transform:basis",
null, pivot.transform.basis.rotated(axis, PI/2),
1/speed, Tween.TRANS_QUAD, Tween.EASE_IN)
tween.start()
yield(tween, "tween_all_completed")
## Step3: Finalize movement and reverse the offset
transform.origin += dir * 2
pivot.transform = Transform.IDENTITY
mesh.transform.origin = Vector3(0, 1, 0)
Try it, and you’ll notice there’s one problem:
The cube is “squishing” because of the basis interpolation, which is going from 0 to 90 degrees. Since the basis also represents scale, this causes some deformation.
We could solve this in 2 ways. First, we could break up the rotation into two separate tweens, each doing 45 degrees. However, I find this tricky when we want to play around with the different tween transitions.
The other way is to ensure the scale remains constant. We can do this by connecting the Tween’s tween_step signal, which fires every frame during the tween, and normalizing the scale. The orthonormalized() method does this:
func _on_Tween_tween_step(_object, _key, _elapsed, _value):
pivot.transform = pivot.transform.orthonormalized()
Alternatively, you can call set_disable_scale(true) on the pivot node).
If your cube’s texture isn’t symmetrical, you may notice that it’s resetting after every roll. To preserve the rotation of the mesh, add the following:
In Step 1
Change mesh.translate(-dir) to mesh.global_translate(-dir).
In Step 3
Add two lines to keep the mesh rotation after reset:
## Step3: Finalize movement and reverse the offset
transform.origin += dir * 2
var b = mesh.global_transform.basis ## Save the rotation
pivot.transform = Transform.IDENTITY
mesh.transform.origin = Vector3(0, 1, 0)
mesh.global_transform.basis = b ## Apply the rotation
Checking for collisions
If you plan to have obstacles in your game, you can check for collisions before moving (similar to any other grid-based movement scheme). Add a raycast check before Step 1 of the move:
# Cast a ray before moving to check for obstacles
var space = get_world().direct_space_state
var collision = space.intersect_ray(mesh.global_transform.origin,
mesh.global_transform.origin + dir * 2.5, [self])
if collision:
return
You could also use a RayCast node. Just remember to call force_raycast_update() before checking.